OTITIS MEDIA
Definition
Otitis media Otitis media is the inflammation of the mucous membrane of the middle ear, eustachian tube and mastoid process. This is called as Otitis Media (Middle Ear Inflammation)
Types of Otitis Media
-
- Acute Otitis, Media
-
- Serous Otitis Media
-
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media.
Acute Otitis Media
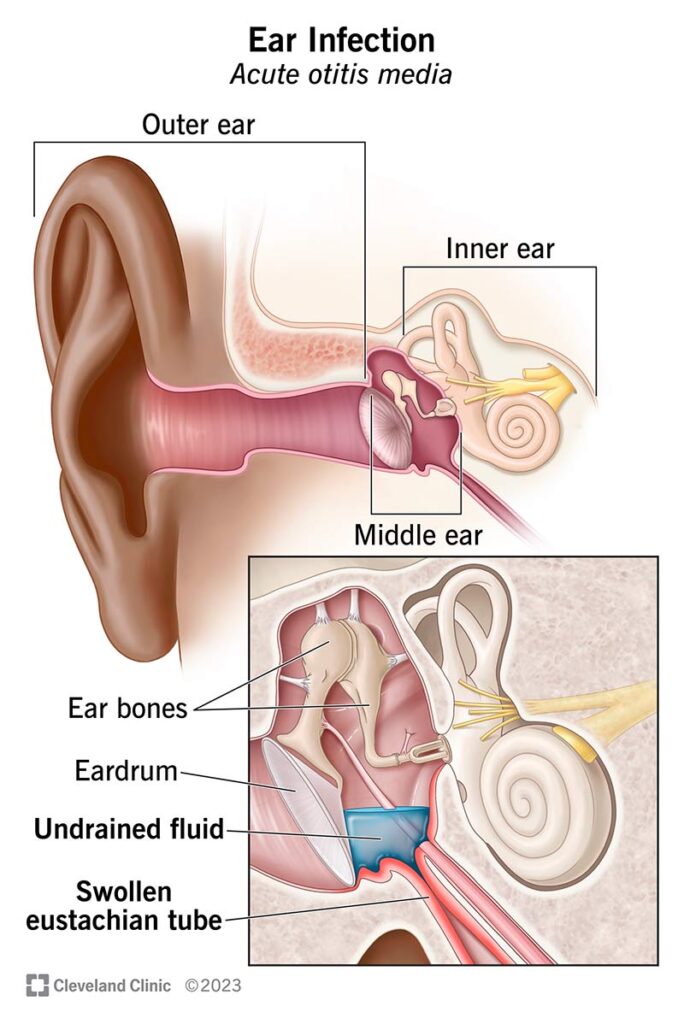
1. ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA
Definition
Acute otitis media is an acute infection of Middle Ear usually lasting less than 6 weeks. This is ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA
Etiology
-
- Entry of bacteria in middle ear.
-
- Infections of (URTI) upper respiratory tract such as rhinitis, sinusitis.
-
- Inflammation of surrounding tissues of Middle Ear.
-
- Perforation of tympanic membrane.
-
- Allergic reaction, e.g., allergic rhinitis.
-
- Bacterial infections such as streptococcus,pneumonia,
-
- haemophilus influenzae, etc.
-
- High deviated nasal septum.
Risk Factors
-
- Young age
-
- Congenital abnormalities
-
- Immune deficiency
-
- Male gender
-
- Family history of otitis media.
-
- Any Irritant Substance
Pathophysiology
1 • Bacterial infection
-
- Allergic reaction
-
- URTI
-
- Immune deficiency
-
- congenital abnormality
-
- Irritant Substance
-
- Increase bacterial colonization
-
- Increase bacterial adhesion
-
- Decrease mucocilliary defense
-
- Exudates & Edema in middle ear
-
- Altered immune response
-
- Decrease retraction of tympanic membrane
-
- Serous exudates in middle ear (Otitis Media)
-
- Medium for bacterial growth
-
- Pus formation
-
- Rupture of tympanic membrane
-
- Acute otitis media
Clinical Manifestations
-
- Otalgia (earache)
-
- Fever
-
- Hearing loss
-
- Drainage from the ear
-
- Tinnitus (a ringing sensation in ear)
-
- Bulging of tympanic membrane
-
- Erythematous tympanic membrane.
Diagnostic Evaluation
-
- History collection
-
- Physical examination
-
- Mastoid X-ray
-
- Hearing test
-
- Ear drainage culture
-
- Antibiotic sensitivity fest
-
- Otoscopic Examination
Management
-
- Infection Control Through administration of antibiotics, e g, ampicillin, amoxicillin.
-
- Give analgesics (Like aspirin) to relieve otalgia
-
- Administer Anti-inflammatory Drugs
-
- Nasal decongestants.
-
- sucking out ear drainage
-
- Aural toilet
Surgical Management
Myringotomy (Tympanotomy): In this procedure, an incision is made on the tympanic membrane to relieve pressure and to drain serous or purulent fluid from middle ear This is a painless procedure and takes about 15 minutes
Complications
-
- Chronic otitis media
-
- Meningitis
-
- Brain abscess
-
- Difficulty in Balancing
-
- Facial nerve paralysis
-
- Lateral sinus thrombosis
-
- Intracranial complications
-
- Marked mastoiditis.
2. SEROUS OTITIS MEDIA (SOM)
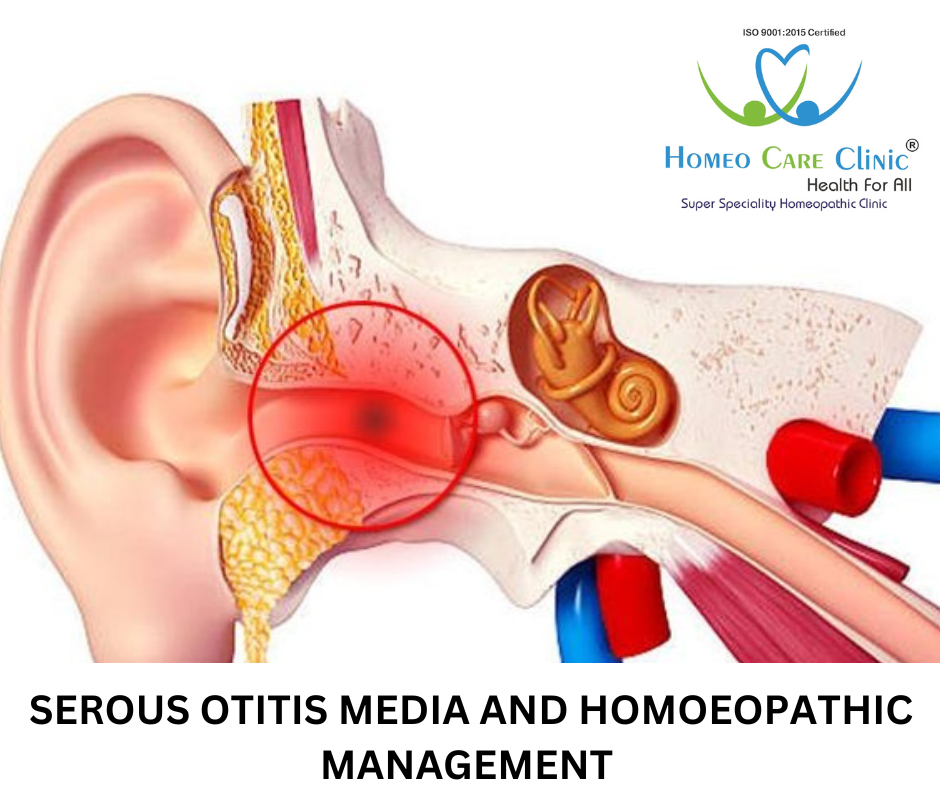
Definition
SEROUS OTITIS MEDIA (SOM) Pus Formation in Middle Ear
SOM (SEROUS OTITIS MEDIA) is a Condition in Which Accumulation of Fluid in Middle Ear without evidence of an active infection. This condition is SEROUS OTITIS MEDIA
Etiology/Risk Factors
-
- Radiotherapy
-
- Barotrauma
-
- Eustachian tube obstruction
-
- Upper respiratory tract infections
-
- Carcinoma of eustachian tube
-
- Allergic conditions
-
- Excessive Production of Earwax
-
- Childhood
-
- Eustachian tube Infection
Pathophysiology
-
- Eustachian tube dysfunction/obstruction and Infection
-
- Barotrauma
-
- Negative middle ear pressure
-
- Serous middle ear transudate
-
- Serous otitis media
Clinical Manifestations/ Symptoms
-
- Hearing loss
-
- Fullness in the ear
-
- Ringing Sensation
-
- Otalgia
-
- Congestive sensation
-
- Popping and cracking noises
-
- Tympanic membrane will appear dull
-
- Air bubbles in middle ear.
Diagnostic Evaluation
-
- History collection
-
- Physical examination
-
- Audiometry
-
- Otoscopy
-
- Audiogram.
Management
-
- Myringotomy
-
- Corticosteroids to reduce edema.
-
- Antibiotics to treat Infection
-
- Analgesics to Relief Pain
3. CHRONIC SUPPURATIVE OTITIS MEDIA (CSOM)3

Definition
CSOM (CHRONIC SUPPURATIVE OTITIS MEDIA) is a condition in Which repeated episodes of middle Ear infection and characterized by irreversible tissue pathology.It is associated with persistent perforation of tympanic membrane.
Etiology/Predisposing Factors
-
- Eustachian tube dysfunction
-
- Antibiotic resistant strain
-
- Arthritis
-
- Granulated tissue.
Pathophysiology
-
- Repeated episodes of acute otitis media
-
- Perforation
-
- Acute otorrhea
-
- Chronic suppurative otitis media
-
- Recurrent Episode of Ear pain
Clinical Manifestations / Symptoms
-
- Hearing less
-
- Cholesteatoma
-
- Pain in ear
-
- Persistent or intermittent foul smelling
-
- Perforated tympanic membrane
-
- Episodes of dizziness
-
- Vertigo
-
- Purulent, mucoid and serous drainage from ear.
Diagnostic Evaluation
-
- History collection
-
- Physical examination
-
- Mastoid X-ray
-
- Otoscopic examination
-
- Culture and sensitivity test. For Ear Secretions
Management
Medical Management
-
- Apply antibiotic powder
-
- Careful suctioning and cleansing of ear
-
- Optic drops
-
- Administer analgesics.
-
- Antiemetics
-
- Systemic antibiotics.
Surgical Management
-
- Tympanoplasty to prevent recurrent infection.
-
- Mastoidectomy to remove cholesteatoma.
-
- Ossiculoplasty: It is a procedure to reconstruct the middle ear bones to Improve and Normal State of hearing.
NURSING MANAGEMENT OF OTITIS MEDIA
-
- Nursing Diagnosis:
“Acute pain in Ear related to inflammation and increased middle ear pressure Observed by Facial Expression,
- Nursing Diagnosis:
Desired outcome:
Patient will experience pain relief.
Nursing Interventions:
-
- Assess the pain by pain rating scale. PPAL, A
-
- Provide comfortable position.
-
- Avoid activity or exposure that aggravate pain.
-
- Encourage patient to take Adequate amount of Fluids and Sof diet
-
- Administer analgesics to relieve pain.
-
- Nursing Diagnosis:
(Impaired Hearing Ability related to auditory nerve damage, infection and
edema of middle ear Observe by absence of respond to sounds Stimuli”
- Nursing Diagnosis:
Desired outcome:
Patient will improve or regain hearing ability.
Nursing Interventions:
-
- Assess patient’s hearing ability frequently.
-
- Reassure the patient and his family members
that hearing loss is not permanent.
- Reassure the patient and his family members
-
- Provide a peaceful and comfortable environment.
-
- Ask the patient and caregivers to notify any discharge from ear.
-
- Encourage caregivers to communicate with patient (Ear Problem) in loud and clear voice.
-
- Administer drugs as prescription.
-
- Nursing Diagnosis:
Risk for infection related to presence of infection possible evidenced by irritability and pain in ear.”
- Nursing Diagnosis:
Desired outcome:
Patient will free from further infection.
Nursing Interventions:
-
- Regular monitoring of ear.
-
- Encourage the patient to take proper nutrition and Increase fluid intake
-
- Avoid contact with person, who is Infected with Upper Respiratory Track Infection
-
- Administer antibiotics, if infection occurs.
-
- Nursing Diagnosis:
“Anxiety related to surgical procedure and potential loss of hearing.”
- Nursing Diagnosis:
Desired outcome:
Patient will be free from anxiety.
Nursing Interventions:
-
- Assess the level of anxiety.
-
- Provide an opportunity for the patient to ask the questions.
-
- Clear all the doubts regarding surgery and its outcome.
-
- Encourage the patient to divert mood.
-
- Provide psychological support to the patient.