MANIER’S DISEASE
Definition
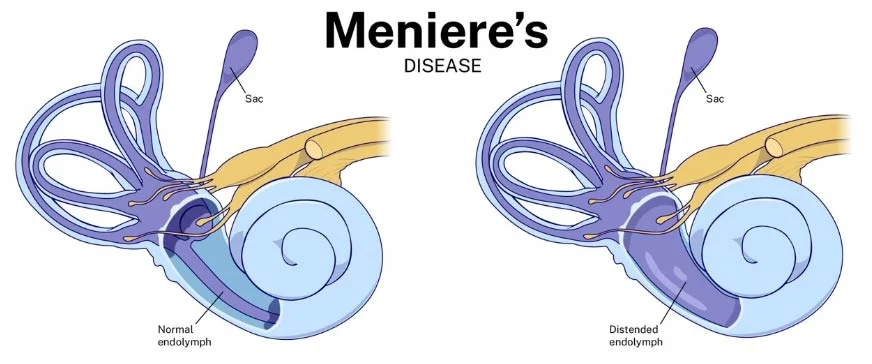
Manier’s disease is an abnormal accumulations of inner ear fluid (too much circulatory fluid or inner ear) caused by malabsorption in endolymphatic sagor
blockage in the duct.
Etiology/Risk Factors
Exact cause unknown.
- virus plays a great role in the etiology but until not proven.
- Fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
Types of MANIER’S DISEASE- Cochlear disease: It is recognized as a fluctuating, and progressive sensorineural hearing loss associated with tinnitus and Inner Ear pressure in the absence of vestibular symptoms or findings.
- Vestibular disease: It is characterized by occurrence of episodic vertigo associated with aural Ear Pressure but no cochlear symptoms.
Clinical Manifestations
- Progressive sensorineural hearing loss
- Tinnitus
- Fullness of Ear
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pressure in the ear
- Vertigo
- Ataxia.
Diagnostic Evaluation
- History collection
- Physical examination Neurological examination
- Glycerol test
- Vestibular test (include caloric test)
- Audiometry
- Weber’s test.
- Tuning Fork Test
Management
Medical Management
- Antihistamine such as meclizine to suppress the vestibular system.
- Tranquilizers such as diazepam to help control the vertigo and Decrease Pressure
- Diuretics to Increase Urine output and Decrease Vascular Pressure
- Provide Vasodilators
- Anticholinergic catropine.
Dietary Management
- Low sodium intake in diet
- Avoidance of alcohol
- Avoidance of aspirin
- Avoid aspirin containing medications.
- Restriction of caffeine,
- Avoid nicotine intake.
Surgical Management
- Endolymphatic shunt
- Vestibular nerve section
- Labyrinthotomy
- Labyrinthectomy.
Ambulatory or Home Care
- Diuretics Use to increase Urine Output
- Vasodilators
- Antiseizure drugs
- Patient education.
Nursing Management
- Prevention of injury
- Assess for vertigo.
- Reinforce vestibular and balance therapy.
- Administer antivertigo drugs
- Encourage the patient to sit down If Feel Vertigo
- Maintaining fluid volume:
- Monitor Fluids – Intake And Output
- Monitor laboratory status
- Assess the signs of dehydration
- Avoid vestibular stimulant Like caffeine
- Administer antiemetics Drugs
- Antidiarrheal medications.
- Adjusting disability:
- Identify the patient’s strengths
- Provide information about vertigo
- Rehabilitation
- Limiting activities to Promote Self Care
- Relieving anxiety:
- Assess the level of anxiety
- Encourage patient to discuss anxiety
- Teach about stress management
- Provide comfort measures.
- Full explanation about disease condition.
- Teaching patient self care:
- Teach the patient to take medications as prescription.
- Encourage the patient to take care of the body
- Teach about coping measures to patient and family members.