Cardiovascular System
-
Introduction
• The cardiovascular system (also called the circulatory system) consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
• Its primary function is to transport oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
• It also helps maintain body temperature, pH balance, and fluid homeostasis. -
Components of the Cardiovascular System
A. Heart
• A muscular organ that pumps blood.
• Located in the mediastinum of the thoracic cavity, behind the sternum.
• Size roughly that of a fist.
• Divided into four chambers:
• Right atrium
• Right ventricle
• Left atrium
• Left ventricle
B. Blood Vessels
• Arteries: carry blood away from the heart (usually oxygen-rich).
• Veins: carry blood to the heart (usually oxygen-poor).
• Capillaries: small vessels where exchange of gases and nutrients occurs.
C. Blood
• Fluid that carries cells, nutrients, gases, and wastes.
• Composed of:
• Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
• White Blood Cells (WBCs)
• Platelets
• Plasma (fluid portion) -
Anatomy of the Heart
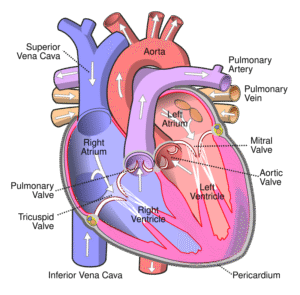
Image Source: wikipedia External Features
• Apex: pointed end, directed downward to left.
• Base: broad upper part.
• Covered by a double membrane called pericardium (fibrous & serous layers).
Internal Features
• Chambers: Right & Left atria (upper), Right & Left ventricles (lower).
• Valves:
• Atrioventricular valves (AV): Tricuspid (right), Mitral/Bicuspid (left).
• Semilunar valves: Pulmonary (right ventricle to pulmonary artery), Aortic (left ventricle to aorta).
• Septum: Divides heart into right and left sides. -
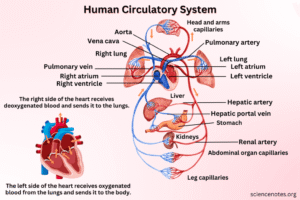
Blood Flow Through the Heart (Circulation Pathway)
• Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium from the superior/inferior vena cava.
• Passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
• Pumped through the pulmonary valve into pulmonary artery → lungs (gas exchange).
• Oxygenated blood returns via pulmonary veins to the left atrium.
• Passes through the mitral valve to the left ventricle.
• Left ventricle pumps oxygen-rich blood through the aortic valve into the aorta → systemic circulation. -
Types of Circulation
A. Pulmonary Circulation
• Heart to lungs and back.
• Purpose: oxygenate blood and remove carbon dioxide.
B. Systemic Circulation
• Heart to the rest of the body and back.
• Delivers oxygen/nutrients; removes waste products.
C. Coronary Circulation
• Supplies blood to the heart muscle itself.
• Coronary arteries and veins. -
Blood Vessels Structure & Function
A. Arteries
• Thick muscular walls.
• Carry oxygenated blood (except pulmonary artery).
• High pressure vessels.
B. Veins
• Thinner walls, valves to prevent backflow.
• Carry deoxygenated blood (except pulmonary veins).
• Low pressure vessels.
C. Capillaries
• Single layer of endothelial cells.
• Site of nutrient and gas exchange. -
Cardiac Cycle & Heart Sounds
Cardiac Cycle
• Consists of systole (contraction) and diastole (relaxation).
• Atria contract → ventricles fill.
• Ventricles contract → blood ejected.
Heart Sounds
• “Lub” = closure of AV valves (start of systole).
• “Dub” = closure of semilunar valves (start of diastole). -
Electrical Conduction System of Heart
Controls heartbeat.
• Key component
• SA Node (pacemaker)
• AV Node
• Bundle of His
• Purkinje fibers
• Generates impulses that cause heart contractions.
-
Blood Components and Their Functions
A. Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
• Transport oxygen via hemoglobin.
B. White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
• Immune defense.
C. Platelets (Thrombocytes)
• Blood clotting.
D. Plasma
• Transport medium for nutrients, hormones, waste. -
Common Cardiovascular Disorders
• Hypertension (high blood pressure).
• Coronary artery disease (blockage of coronary arteries).
• Heart failure (inability to pump sufficient blood).
• Arrhythmias (abnormal heartbeat).
• Myocardial infarction (heart attack).
• Peripheral artery disease (narrowing of arteries).
• Varicose veins (enlarged veins). -
Nursing Considerations
• Monitor vital signs (pulse, BP, respiratory rate).
• Promote cardiovascular health (diet, exercise, smoking cessation).
• Recognize signs of cardiac distress (chest pain, shortness of breath).
• Administer cardiac medications (beta blockers, diuretics, anticoagulants).
• Postoperative care for cardiac surgeries.
• Educate patients about disease prevention and medication adherence.