The Eye: A Structural and Functional Overview
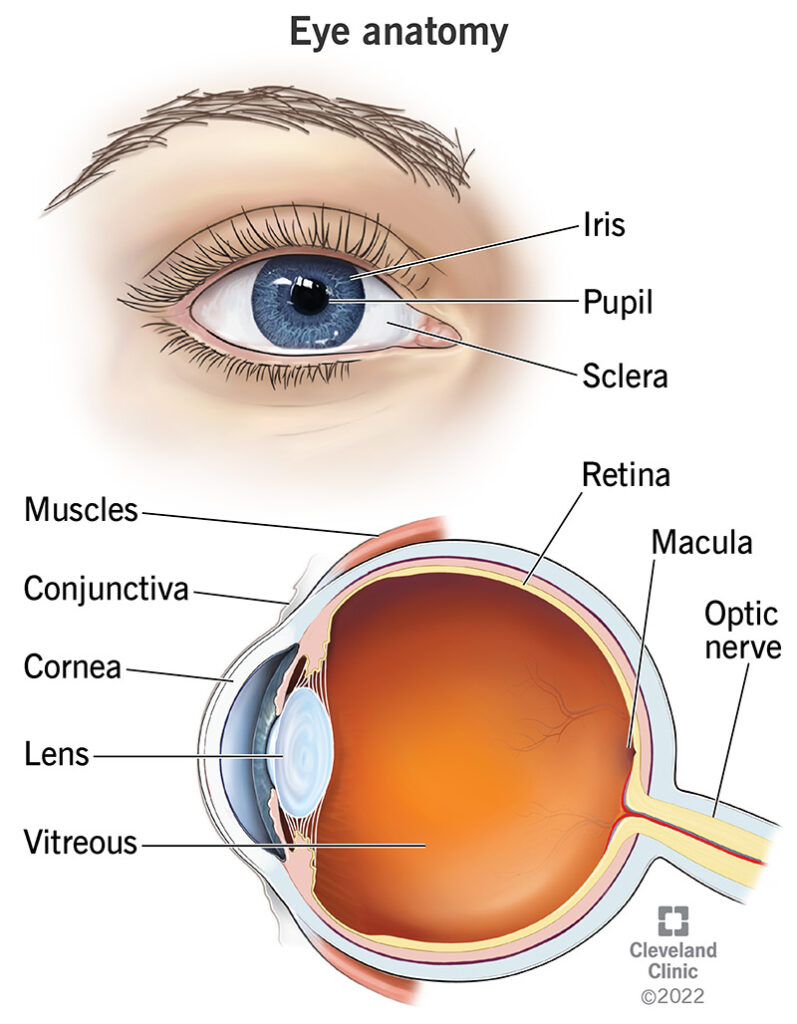
Eye is the organ of sense of sight. It is supplied by optic nerve. The eyes ball are Situated within the orbital cavity of Face. The eye ball is spherical shaped and The Eye ball covered with Adipose Tissue to Prevent Injury.
The bony wall of the orbital cavity also protects the eyes from injury. Eye ball Diameter is 2.5 cm. The other structures within the eyeball are lens, vitreous body, aqueous fluid etc
STRUCTURE OF EYE
The eye consists of three layers:
- Fibrous Tunic
- Vascular Tunic
- Retina
- Fibrous Tunic
This is a outer or superficial layer of eyeball and consists of:
- Cornea: This is a transparent layer. It continuous with sclea layers of sclera.
- Outer layer: Made by non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
- Middle layer: It consist of fibroblasts and collagen fibers
- Inner layer: It consist of simple squamous epithelium
- Sclera:
— It is the white of eye
— This is a dense connective tissue layer
— It cover whole eyeball except cornea - It protect the internal organs of eyeball
Sclera makes the shape of eyeball.
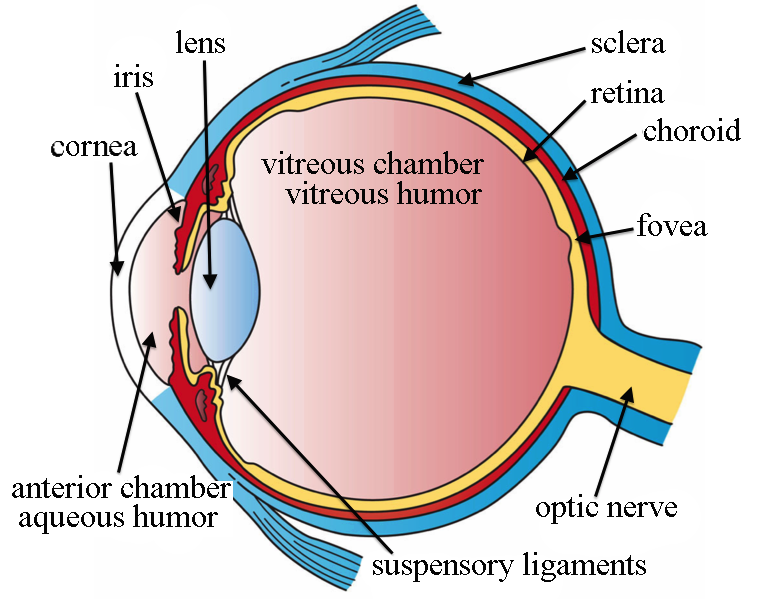
- Vascular Tunic
- It is also called as uvera
- It is a middle layer of eyeball
- It consist of choroids
Choroid
- It is present just internally to sclera
It is highly vascularized part
The color of choroid is deep chocolate
brown - After entering light in eye absorbed by choroids.
Ciliar Boby
- This part consists of ciliary muscles
- It is the anterior continuation of choroids
- It provides attachment for suspensory ligaments.
IRIS:
- visible & colored part of the eye
- It is flattened donut in shape
- It separates the anterior segment is anterior and posterior chamber
- Eye Colour is depends on the amount of melanin Hormone present in it.
- Retina
- This is inner layer of eyeball
- It consists of:
- nerve cell bodies
- axons.
- Pigmented layer
- Neural layer
There are many layers of retinal neurons
as below:
- Photoreceptor layer
- Bipolar cell layer
- Ganglion cell layer
- Rods and cons are sensory receptors cells and contain photo sensitive pigments.
- The action of photo sensitive pigment is conversion of light rays in to nerve impulse.
ACCESSORY ORGANS OF EYE
There are many accessory organs of eye:
Eyelids
- Also known as palpebrae
- The eyelids protects the eye from:
- dust
- foreign bodies
- insects
- Help in sleep
- Secrete lubricants on the eyeball
Eyelashes and Eyebrows - Extends from border of eyebrows
- Protect the eyes from:
- sun rays
- perspiration
- foreign objects
- The sebaceous ciliary glands are present at the hair follicle of eyelashes release a lubricant fluid
The Lacrimal Apparatus
This apparatus consist of organ that involve in the production and draining of tears
Extrinsic Eye Muscles
There are total six extrinsic muscles involve in moving of eye:
- Inferior rectus muscle
- Lateral rectus muscle
- Medial rectus muscle
- Superior Oblique muscle
- Superior rectus muscle
- Inferior Oblique muscle
BLOOD SUPPLY TO EYE
- Arterial blood is supply by central retinal artery and ciliary arteries of eye
- Venous drainage – central retinal vein
It consist of (for each eye):
- 1 lacrimal sac
- 2 lacrimal canaliculi
- 1 lacrimal gland and duct
- 1 nasolacrimal duct.