Acute Otitis Media
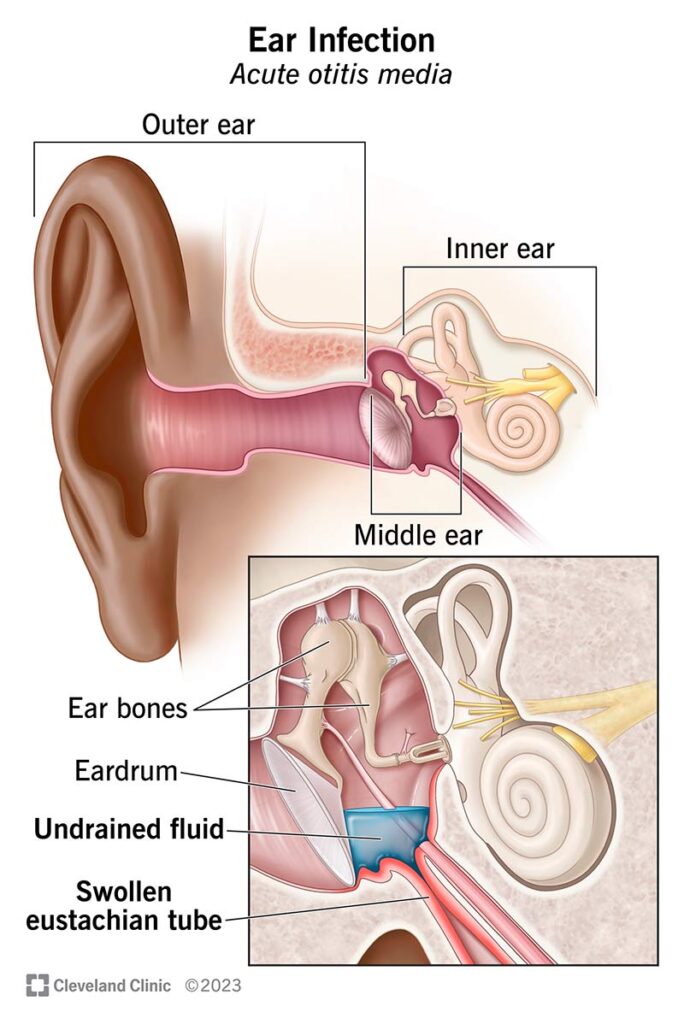
Otitis media
Definition
Otitis media Otitis media is the inflammation of the mucous membrane of the middle ear, eustachian tube and mastoid process. This is called as Otitis Media (Middle Ear Inflammation)
is the inflammation of the mucous membrane of the middle ear, eustachian tube and mastoid process. This is called as Otitis Media (Middle Ear Inflammation)
Types of Otitis Media
- Acute Otitis, Media
- Serous Otitis Media
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media.
ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA
Definition
Acute otitis media is an acute infection of Middle Ear usually lasting less than 6 weeks. This is ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA
Etiology
- Entry of bacteria in middle ear.
- Infections of (URTI) upper respiratory tract such as rhinitis, sinusitis.
- Inflammation of surrounding tissues of Middle Ear.
- Perforation of tympanic membrane.
- Allergic reaction, e.g., allergic rhinitis.
- Bacterial infections such as streptococcus,pneumonia,haemophilus influenzae, etc.
- High deviated nasal septum.
Risk Factors
- Young age
- Congenital abnormalities
- Immune deficiency
- Male gender
- Family history of otitis media.
- Any Irritant Substance
Pathophysiology
1 • Bacterial infection
- Allergic reaction
- URTI
- Immune deficiency
- congenital abnormality
- Irritant Substance
- Increase bacterial colonization
- Increase bacterial adhesion
- Decrease mucocilliary defense
- Altered immune response
- Exudates & Edema in middle ear
- Decrease retraction of tympanic membrane
- Serous exudates in middle ear (Otitis Media)
- Medium for bacterial growth
- Pus formation
- Rupture of tympanic membrane
- Acute otitis media
Clinical Manifestations
- Otalgia (earache)
- Fever
- Hearing loss
- Drainage from the ear
- Tinnitus (a ringing sensation in ear)
- Bulging of tympanic membrane
- Erythematous tympanic membrane.
Diagnostic Evaluation
- History collection
- Physical examination
- Mastoid X-ray
- Hearing test
- Ear drainage culture
- Antibiotic sensitivity fest
- Otoscopic Examination
Management
- Infection Control Through administration of antibiotics, e g, ampicillin, amoxicillin.
- Give analgesics (Like aspirin) to relieve otalgia
- Administer Anti-inflammatory Drugs
- Nasal decongestants.
- sucking out ear drainage
- Aural toilet
Surgical Management
Myringotomy (Tympanotomy): In this procedure, an incision is made on the tympanic membrane to relieve pressure and to drain serous or purulent fluid from middle ear This is a painless procedure and takes about 15 minules
Complications
- Chronic otitis media
- Meningitis
- Brain abscess
- Difficulty in Balancing
- Facial nerve paralysis
- Lateral sinus thrombosis
- Intracranial complications
- Marked mastoiditis.