OTITIS EXTERNA (SWIMMER’S EAR)
Definition
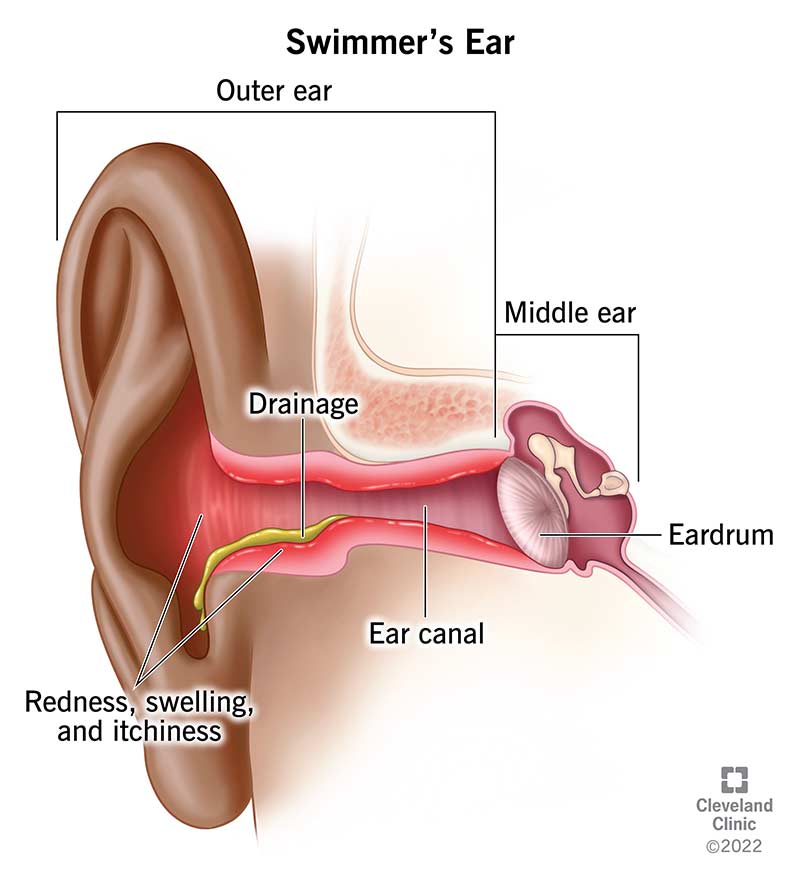
Otitis Externa (Inflammation in External Ear)
Otitis Externa is a condition that causes inflammation in external Auditory canal that runs from eardrum to the outside of the ear. This condition is known as otitis externa. simply known inflammation of external ear.
Causative Agents
these are some causative agent
- Pseudomonas Aeruginosa (about 40%)
- S-epidermidis
- S. aureus
- Aspergillus spp (fungal infection)
Etiology
- Use of fingers,pen, pencil, paper, cotton swab, hairpins or any foreign object to clean ear.
- Swimming – because the water come into ear
- Narrowing of ear canal.
- Skin disorders such as psoriasis, eczema.
- swimming in water
- Frequent showering use in bathing
- Cleaning ears too frequently
- Using headphones or a hearing aids and other objects
- Skin allergies
- Eczema (it is a skin disease)
- Skin irritation from hair products like shampoo, hair oils,
- Kids and teenagers
- Use of pen, pencil, paper, pen caps, hairpins, fingers for clean skin
Risk Factors
- Children
- Smoking (other bad habits)
- Seasonal allergies
- Cold or upper respiratory tract infections (URTI)
Pathophysiology
1 • Repeated exposure of water
- Trauma or injury to ear canal
- Blockage in ear canal by any foreign body
- Skin disorders like Eczema
- Disruption in the external auditory canal’s
protective mechanism - excessive growth of pathogen
- Inflammation and pain
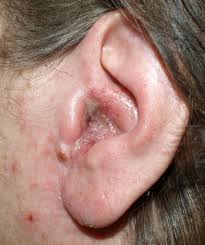
- Erythematous (red skin), swollen, tender and warm skin
- Debris and discharge accumulation in ear canal
- Entrapment of pathogens
- Propagating the infective process
- Infection within External auditory canal
Clinical Manifestations
- Itching sensation in ear
- Difficulty hearing
- Drainage of pus or fluids (discharge) from ear, drainage from ear
- Tenderness inside ear (pain produce by compress the ear area)
- Pain while rotating head
- Bad smell from ear
- Pain or discomfort in the ear
- Redness and warm skin
- Swelling and tenderness in ear canal
- Diminished hearing (lowering power of hearing)
Diagnostic Evaluation
- History collection
- Physical examination
- Otoscopy
- Tympanometry to evaluate how well ear is functioning
- Simple hearing test
- Complete blood count (cbc)
- Blood culture
Management
- Clean the outer ear carefully.
- Apply anti-nflammatory and anti-microbial drugs
- Oral antibiotics to treat infection.
- Antibiotic drops use to treat bacterial infections in external car .
- Steroid drops to reduce swelling in ear
- Administer analgesics such as acetaminophen(paracetamol),ibuprofen to relieve pain of ear
- Antifungal ear drops if fungus is the cause of infection in ear
- Keep ears dry and prevent from water
- Avoid use of headphones or a hearing aid and other materials
- Ear wicks are used, if swelling in ear canal is very severe
- Administer oral or IV antibiotics if infection is severe
Complications
- Chronic otitis externa
- Malignant otitis externa
- Permanent hearing loss
Prevention
- Use a clean cloth or towel for cleaning of ear
- Before the use of hearing aids , it should dry and clean
- Use of earplug or a bathing cap, when swimming
- Dry ears after swimming or showering
- Avoid scratching in the ear
Pingback: OTITIS (inflammation or infection of the ear)